Concept art from The Art of Portal 2.
Tag: character design
Untitled
Character concept art from The Art of Portal 2.
Varying Your Body Types
By me, Sara D. (Heh.)
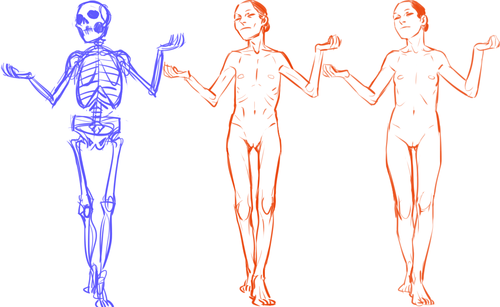
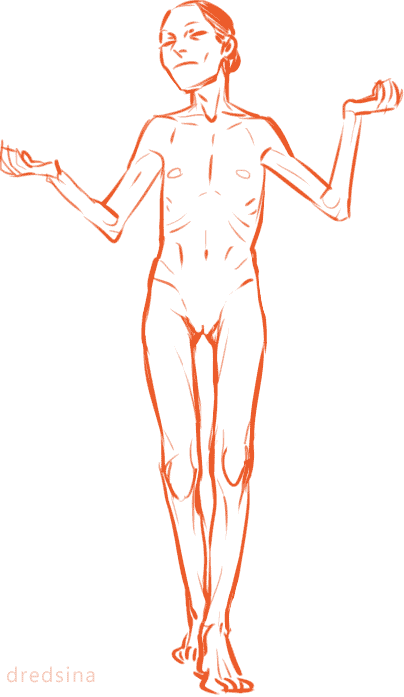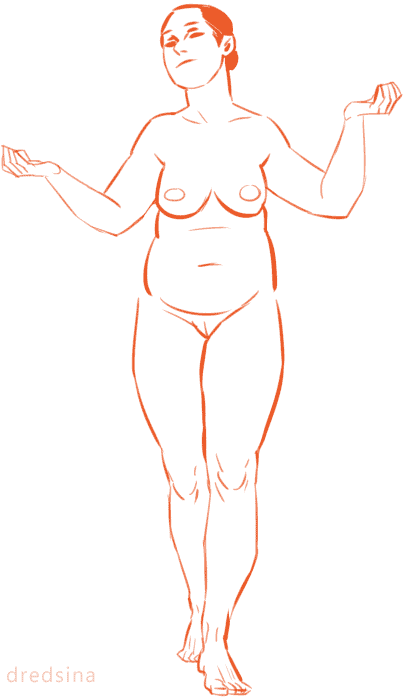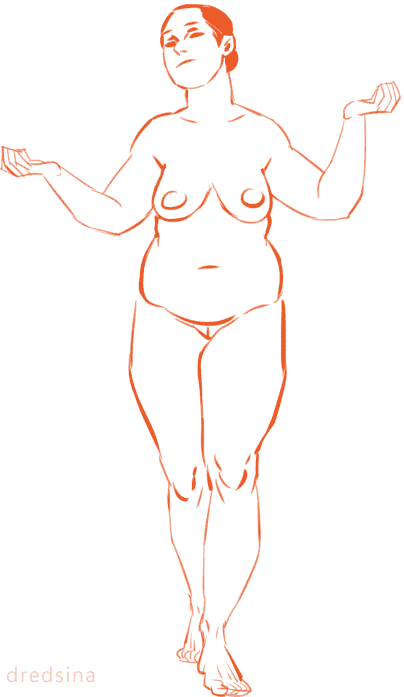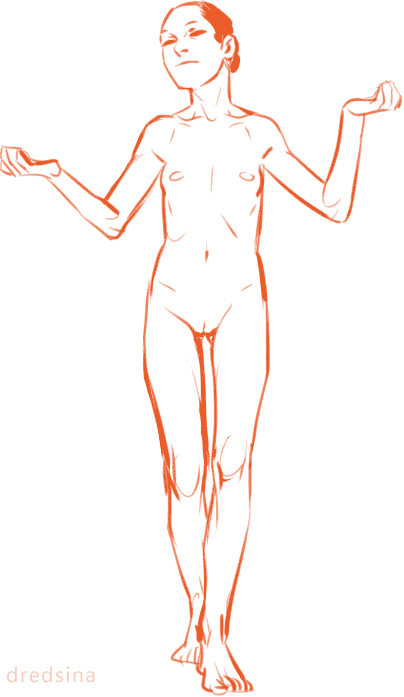
I think it’s very important for artists to vary the types of bodies they draw! Not only does it add visual interest and diversity, but different body types can enhance your characters! (Plus it’s more realistic; when was the last time you walked down the street and everyone had the same body type?) I know I have a hard time drawing different bodies, especially with men, so I’m making this tutorial to teach myself as well (I’ve heard the best way to cement learning something is to teach someone else).
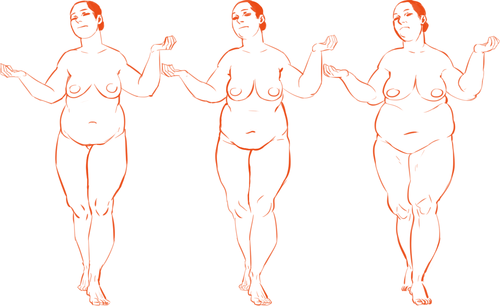
So! Bodies! I’m going to use women for this tutorial because I feel they have more variety in their bodies. One of the most obvious ways bodies differ is in their amount of fat.
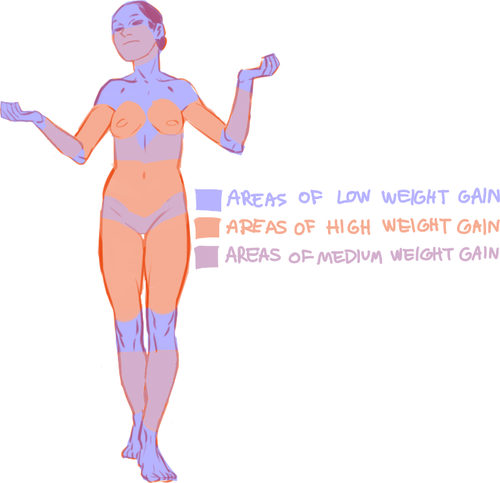
On average, people store fat mostly in core areas like the bust, the waist, and the hips. It is important to remember that people gain and lose weight differently, and this is true no matter how fat or skinny one gets. However, these are common places people store fat:
The face and neck can be immediate indicators as to how much fat the rest of the body has; when someone loses or gains weight, it’s initially obvious in the face. This is possibly because the eye is (usually) drawn first to the face.
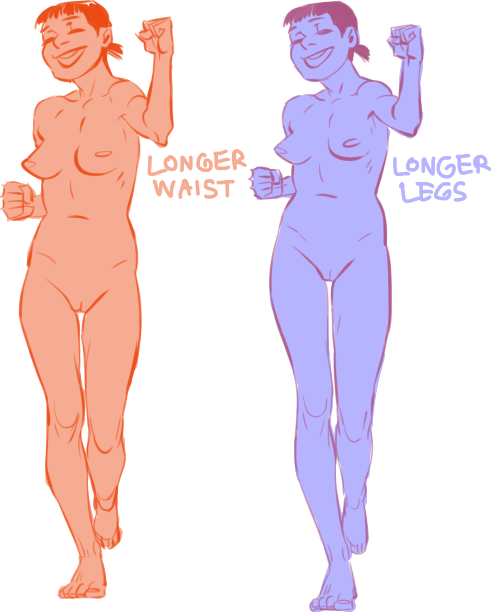
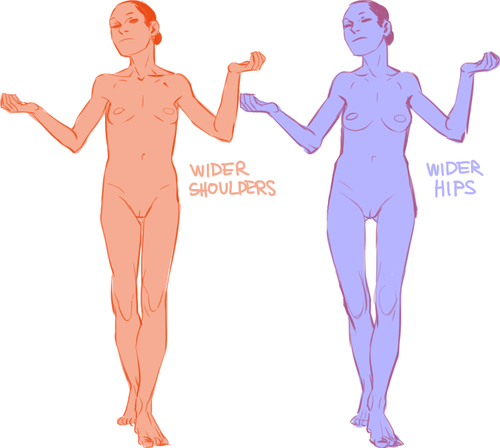
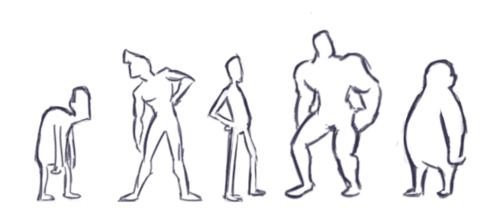
In addition to differences in the amount of body fat, bodies vary vastly in their proportions. The two main ways they differ is skeletally and in fat distribution. The hip to shoulder ratio is skeletal, and someone with wider shoulders might look more powerful or masculine, and someone with wider hips might look more grounded or feminine.
The torso to legs ratio is also a skeletal ratio. Someone with long legs in comparison with their torso might look taller than someone of the same height with a long torso, and they might also look skinnier.
(I say as I finally get some visual variety all up in here.)
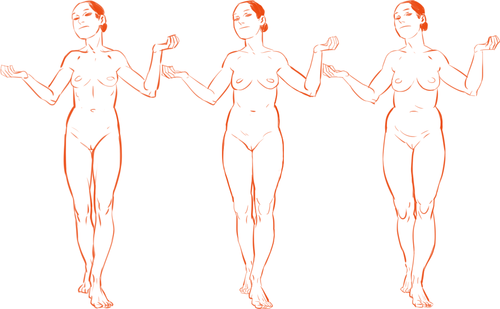
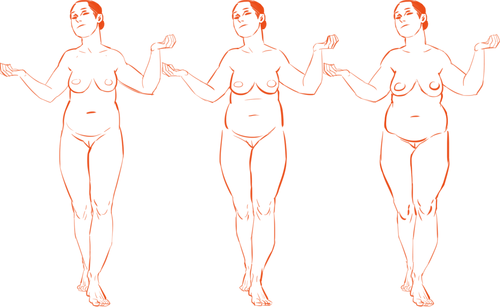
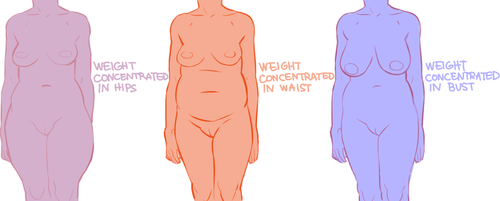
Because the hips are also one of the places with the most weight gain in women, large hips can also be a matter of fat distribution. The three main places where the fat ratio really matters is in the bust, the waist and the hips (making up the core of the body).
While men usually carry weight in the belly area, the fat distribution can really vary with women. Some women carry more weight in the bust, some in the belly, and some in the hips/thighs. Some women carry more weight in two areas, like the bust and the hips, the bust and the belly, or the belly and the hips. Some women show no obvious bias to any area and carry weight equally.
Taking into account skeletal ratios, fat distribution patterns, a vast human weight range, muscle tone and age, there are endless permutations of body types. It would be a shame if you used only one!
Oh, and that first image looks really interesting as a gif.
Untitled
Learning anatomy drawing is important. Period. Whatever you plan to draw and however you plan to draw it you need to have an idea of what it actually looks like, practice in realism, before you plan to move on to creative interpretation.
Here are examples of all different kinds of athletic body types to illustrate the importance of knowing what sort of “built” look you will need to go for when drawing and designing a character. Not all fit is the same fit and it is so hard to find adequate variety when looking for references. These were linked by a talented comic artist Nina Matsumoto. Here site can be found here http://ninamatsumoto.wordpress.com/
A good sampling of her art can be found here http://spacecoyote.deviantart.com/
Untitled
A page from the character bible I’m making for Sister Claire characters. I’ll keep posting these as I finish them. =)
5 Essential Superhero Redesigns!
Seeing as how I’ve done both the top ten for best and worst superhero costume redesigns, I feel obligated to put my money where my artistic mouth is and take a stab at fixing or updating some of these costumes. I’ll be taking a similar approach to my earlier take on Batman & Robin, where both the back story and design of each character are fair game. I’ve done five here, and chose them based on one of two criteria:
- It’s a particularly awful outfit that doesn’t fit the character, or
- It’s a solid character who just needs some updating or tweaking
I’ll list these in order of “reboot depth:”
5. Starfire
What’s wrong: In the wake of DC’s “new 52” this felt like a no-brainer. Starfire is a decent character who’s always, in my opinion, gotten the short end of the costume stick. I get that she’s supposed to be sexually liberated and somewhat polyamorous, and that’s fine, but dressing like a John Carter’s Princess of Mars-themed stripper doesn’t cut it. Really, up until the Teen Titans cartoon she’s always been in the most awkward and impractical getups for someone fighting crime.
The Fix: I went for the simple route and took some notes from the cartoon (notably the skirt). I wanted to make sure it kept the bubbly, innocent feeling of the character while also hinting at some power (with the exposed arms here). The overall effect is meant to convey someone who’s tough, cheerful and comfortable flying around in the air.
4. Dr. Strange
What’s wrong: I love Dr. Strange, but he’s always had the worst outfits. For a guy who basically hangs out in his house in the West Village, he seems to always wear the most ostentatious getups. He’s not an alien from another planet or from some culture that would dress that way, he’s a grown man who became a wizard well into adulthood. Nothing wrong with having some style while you’re maintaining the balance of the mystic planes.
The Fix: Two parts Vincent Price, one part Christopher Lee and one part Dr. Orpheus, this Dr. Strange is still magical, but with a more coherent design direction.
3. Ms. Marvel
What’s Wrong: Simply put, I think it’s embarrassing for Marvel to showcase a prominent character like Ms. Marvel and have her wearing that outfit. It’s just so tacky, and tells us nothing about the character. Basically they just changed the colors of Jean Grey’s Phoenix costume and exposed more skin. Come on, guys.
The Fix: Since her origins are ostensibly tied with Captain Marvel, I decided to go a route that’s more along the lines of the Ultimate Marvel version of that character, where her abilities come from alien technology rather than vague space magic. The notion that she’s, for example, permanently bound with this technology that she doesn’t fully understand can make for some interesting stories. There can be some potential with this character again with just a little bit of tweaking.
2. Wonder Woman
What’s Wrong: Wonder Woman, in my opinion, is a character that’s always been on the cusp of being really neat but never quite making it like Superman or Batman. Although a feminist pop icon, her origins are too tied up with creator WIlliam Marston’s obsession with bondage. Because of this (and an all-too-frequent parade of poor or sexist writing), she’s never had a solid, progressive design. The 21st century can update this character.
The Fix: One part Thor, three parts Xena. I’d push the mythological angle further. Just as nobody thinks of Thor as “Superman with a hammer” I don’t want Wonder Woman to be “girl Superman,” as she’s sometimes seen. I’ve also tweaked her origin slightly, making her a more literal “statue come to life.” This isn’t as extreme as it seems: in regular canon, Wonder Woman’s origin was that she was formed out of clay by the queen of the Amazons, and imbued with the powers of the Greek Gods. (Note: I am well aware that Greek statues were painted, but for aesthetic & thematic reasons it doesn’t work here. She’s just an old statue, so there wouldn’t be paint.) This, I think offers more story possibilities if she’s less literally human, physically. Her personality would remain the same (nothing more fun than the perspective of an Amazon in the modern world), but we now have an added Greek layer of Pygmalion or Telos.
The costume change is mostly conservative. Because of the strong fetish associations (and overall impracticality for a fighting Amazon), I’ve removed the lasso in favor of more traditional Greek weapons. The overall effect is intended to push Wonder Woman’s core themes further while making her also stand out as more than just “the female superhero.”
1. Superman
What’s Wrong: Since his creation, Superman’s drifted from being a progressive champion for the common man to a patriotic middle-America boyscout who represents the establishment and traditional values. When he was developed in the 30s, Superman was very much a Depression-era hero, mostly going after villains like crooked money lenders and saving people who were being abused by the system. His superpowers came from the fact that he was from a more advanced society, and his morals too were because he was simply a brainier, more sophisticated guy. During and following WW2 and into the Cold War, though, he became an official symbol for American values in particular (it was originally “Truth and Justice,” without “the American Way”). He was now not just an alien, but an alien raised by simple Kansas farmers and his abilities had a more generic “superpower” explanation. This is all fine, really, but I think the original concept is more compelling these days.
The Fix: Two parts Martian Manhunter and Ten parts Fleischer Superman. “Superman: the Man of Tomorrow, Strange Visitor from Another World.” I really want to push that. First off, Kryptonians should actually look like aliens and not white people. Here I have Kal-El from a race of beings whose technology and biology are long since indistinguishable (Clarke-esque space gods, you know the type). They’re strange to our mortal eyes but mean well. I’d keep the “destroyed planet” origin but more heavily emphasize the “non-interference” part of Superman’s mission statement.
If you’ll remember from the 70s movie, his father Jor-El told him he was forbidden to interfere with the course of human history, but when you think about it, that’s kind of vague. What I’ve done is added a Star Trek or Uatu the Watcher kind of prime directive to all advanced species: Kal-El can’t let people know that he’s an alien, nor can he openly interact with them using advanced technology. Still, he’s a compassionate guy and wants to help, so he takes the form of “Superman” to inspire the mortals in a constructive way. Also, the notion that he can take on different forms means that the Clark Kent secret identity need not be as bad as it currently is.
The costume redesign holds to the basic themes but makes it a little more working class. The buttons at the top are meant to invoke overalls, and the sleeves are cut a little higher for someone working with their hands. I’ve removed the spandex and gone with looser fitting slacks, while keeping a short cape and boots, since he’s still an adventurer.
Overall I want to evoke a classic Superman feel while making it a little more modern in its exploration of the sci fi themes. He’s still basically the same guy: an alien from another world looking to fight injustice, but without the overt patriotism and a quirkier execution of the secret identity.
*********************
So there you have it. I’ve hope you’ve enjoyed my superhero costume trilogy!
Figures: They Speak For Themselves (mildly NSFW)
Continued from the last article about costume design, today we’re going to talk about those wacky things you hide underneath clothing. Figure drawing is a pivotal tool to any artist, but being able to effectively render humans and creatures is only part of the equation. Even if your draftsmanship is solid, you won’t get far if your designs are uninteresting. Effective and dynamic figures are the cornerstone of having compelling characters in pretty much any comic.
The Purpose of Character Design
The focus of art in general is to generate a particular response out of your audience; the mechanics of what you literally create are often secondary to this goal. Something can be abstract or literal, but the point in both cases is the effect is has on the viewer/listener/reader; the creation itself is a means to an end. In comics, authenticity and realism are not defined by what you are actually drawing, but rather how your drawings are viewed by your reader. In the context of a visual narrative, a simplistic drawing can be “more real” than a more realistically rendered one if that simplistic drawing evokes a more authentic response. A stickman can be a more convincing character than a photorealistic painting; it all depends on how that stickman is conveyed.
When you design your characters, you have an opportunity to both communicate information about them, as well as provide a conduit through which information about other characters and even environments can be shown. Their appearances can augment the actions in the narrative, or even take the place of regular action.
Focused Caricature
When designing characters for comics, then, it’s not universally important to faithfully recreate how people look in real life or even caricature real life. This may sound contentious at first glance. After all, isn’t a big part of cartooning exaggerating elements of real life? Certainly, but that’s only half of the equation when it comes to visual narratives. A regular caricature is mostly about emphasizing what’s visually obvious, and while that’s still present in comics and animation, on top of that there’s often the need to convey information about the character. Even if you’re basing a design on a real person, what you choose to emphasize can determine how the audience views that character. Again, what part of “reality” (in this case people’s appearances) you select to share can profoundly change how those characters are perceived.
Implied Motion
While they can be very similar, a fundamental difference between the needs of comic design versus animation design is the presence of literal motion.
In animation you can give your character a nervous tick, a particular walking pattern, or any other number of facial and other motion cues to add flavor and depth to a character. However, with the static images of comics, this approach is limited. As such, more pressure is placed upon the designs themselves because they’re the primary visual resource the reader has for gaining information about the character. Luckily, there’s a plethora of tools at our disposal for doing just that. The shape, size and position of a figure can be designed in such a way that it implies motion. Upturned brows and lips can suggest someone who is frequently bemused, an exaggerated posture can give the impression of a certain type of gait, and so on. And since the reader’s eye can dwell on a comic panel indefinitely (at least in theory), there’s more freedom to employ subtler facial and body elements to add to a character’s flavor.
The Body
Shape Up
Silhouettes and overall shape are the first pieces of information to reach the reader, and because of this they will always dominate any character’s design. If your silhouette isn’t doing its job, the rest won’t matter. Starting with a simple, clear shape and working backwards is a good rule of thumb. And while this is naturally easier with monsters and other fantastical creatures, it applies just as much to regular people.
Body Types
People are not divided into skinny/fat/muscular. While these body states do obviously exist, each of these will still differ from person to person. For example, there’s not a single “athletic” body type, but dozens (as this amazing photo series shows). Don’t fall into the trap of old superhero comics where everyone looks like a bunch of clones wearing different costumes. People’s builds, postures, hands, feet and musculatures are extremely diverse, going far beyond simple factors like age, height and weight.
Body Language
Your character’s motions can inform you quite a bit on how you could design their form. If a character often stoops or shuffles, you can warp his or her spine and posture to bring attention to that sort of behavior. In general, you want the figure to emphasize and accentuate the type of body language indicative of that person. This is really important. In animation, there’s a little less of a required connection between body language and design because you can literally show motion, but with comics being a static medium, you have to imply a lot of motion without showing it. Naturally, if your character has a very wide range of motion, your design should reflect that too. Main characters aren’t usually designed around a single posture, for example, but side ones often are. In the end, this is all a tool to efficiently communicate information about a character to the audience.
The Head
Shapes Again
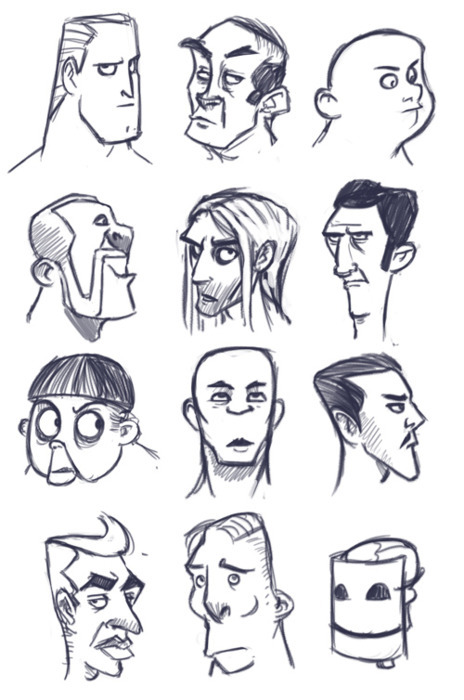
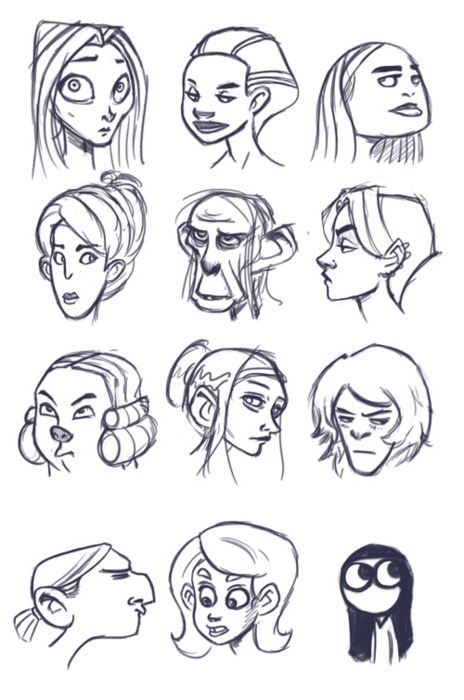
Even more so than with the body, you should be able to reduce each character’s head to a fairly recognizable shape. This is the foundation for developing a good head silhouette, which is vital because the focus of a page is often on peoples’ faces; recognition should be established on a subconscious level with little to no effort on the part of the reader.
If the reader can’t immediately and clearly distinguish who is who without using details, the designs are bad. Also note: using hair alone to distinguish heads is cheating. Similar to the superhero body problem, don’t fall into the crappy anime trap of having identical heads that are only distinguishable by their wacky hair. Obviously hair is a component of character design, but to rely exclusively on it is taking a shortcut that only ends in sloppy composition and no variety.
Similar to the Naked Test (which we’ll talk more about shortly), you should be able to immediately distinguish all your character’s heads without any adornments or hair. Shave ‘em down and compare.
Variety is Your Friend
Ears, eyebrows, skulls, eyes, eyelids, noses, cheekbones, nostrils, hairlines, necks- these are all elements that will vary from person to person. Don’t be afraid to go beyond normal human proportions. Exaggerating or simplifying to the point of even being a stickman is perfectly fine, so long as it suits what you’re trying to do.
Dominant Expressions
What types of facial expressions and body language do your characters exhibit? Main characters generally require more of a range than side characters, while less three-dimensional characters can be designed to fit only a handful of expressions.
A lot of character information can be shown to the audience this way. Showing rather than telling your readers means you’re playing to the medium’s strengths.
The Naked Test
Once you’ve designed your figures, we move on to the Naked Test. When developing a cast or even just a couple of characters, they should always be instantly recognizable without the aid of clothing. Even if their clothes have some key distinguishing elements to them (which they probably should), the bodies themselves are the foundation, and if the foundation is too generic, then you’re left with a flat design that can’t be corrected by adding stuff on top. All the basics should be present at this level: distinguishable silhouettes, unique body types and proportions, and unique facial shapes should all be there to tell your character’s story.
Figure drawing isn’t easy. Because we’re hard-wired to distinguish even the tiniest variance in human appearance, there’s a lot of pressure to get figures right compared to other subjects. As such, it’s easy to play it safe with conservative designs that don’t strain our draw-muscles, but it’s important to push past that. Effective and compelling character design is a skill that’s indispensable for cartooning of every kind.
Costumes: the Wearable Dialog
I mentioned before some of my favorite character designs in the world of comics and have been meaning to tackle this subject again. I came to realize, however, that “character design” is itself a fairly massive subject, and that it would be best to break the topic down into separate installments. Today, true believers, we’re going to talk about outfits and costumes, which are often a pivotal part of a character’s design.
3 Essential Questions
Clothing can convey quite a bit of conscious and unconscious information to the reader, but it should never be doing 100% of the legwork. Body language, shape and overall behavior all come into play when building a character, and the trick is to figure out what clothing can do that these other elements can’t. To get started, it’s important to ask some basic questions about your character before jumping into costume design.
1) Costume Hierarchy
How often does this character appear? Is it a main character or a side one? Primary characters have more complex needs than side characters, which is to say that the more information you have about your character, the more that can be conveyed in their appearance. Additionally, the more frequent the character appears, the more versatile the design needs to be.
2) Environmental Relationship
If it’s a side character that only ever appears in one setting, for example, you need only design the outfit to fit in that environment. If they are a main character, though, chances are you’ll need the outfit to mesh with more than one setting.
3) The Naked Test
Is your character recognizable without any clothes on? Body types, especially those of the main cast, should be distinctive even without the help of any outfits. The naked form is the foundation of all character design. Before you start dressing your body, make sure it’s a body worth dressing.
Once you’ve sufficiently answered these questions, it’s time to jump into the actual design phase!
Shape
Every character, no matter how complex, should be designed around an overal unique visual shape. This theme should not repeat in any other character. This shape should be readable enough that if you were to shrink all your characters into a super-simplified cartoony state, they should still be distinguishable. Character designs follow a hierarchy: you grab the reader’s attention with the most essential information and then invite them to investigate the details. If important elements of your design are only evident in the details, then it needs to be reworked. If your character is not completely distinguishable in silhouette, it needs to be reworked. Detail should always radiate from the core theme.
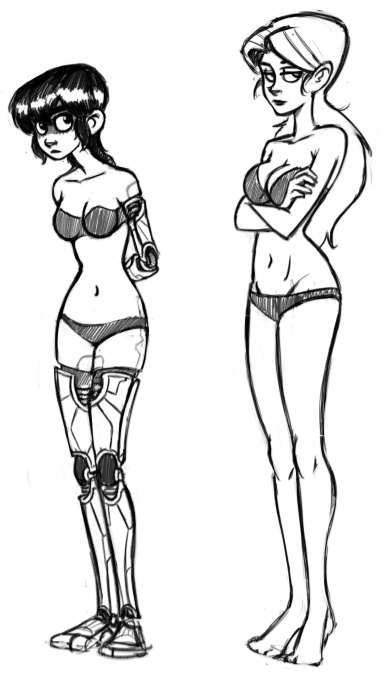
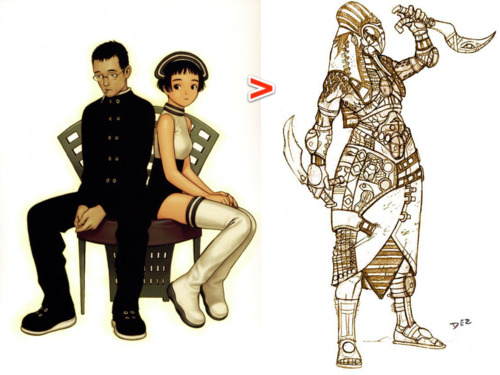
Kim and Vonnie stay distinct in a few ways.
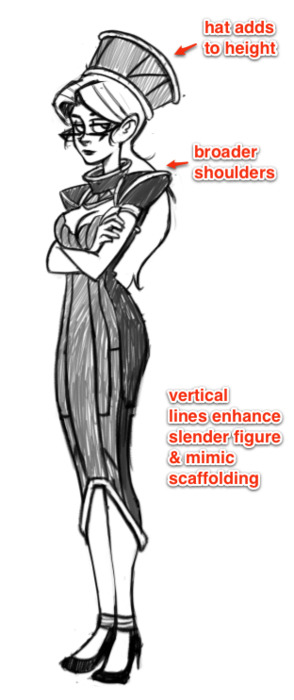
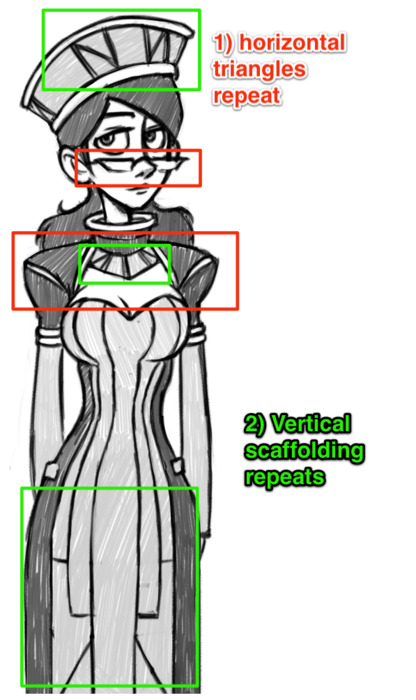
The primary difference in shape between the above two characters is one of curves versus triangles. Vonnie is very angular, and her clothing’s angles mimic the scaffolding of an art deco building to emphasize her height and posture. Kim’s outfit makes her look shorter, but jaunty. There are a lot of soft curves going on there to make her seem younger and more innocent.
Action
What does your character do? In what way would their clothing reasonably convey how they spend their time? This is an easy question if it’s a uniformed occupation, but it certainly doesn’t stop there. A more bookish or socially inept character is often prone to mismatched clothing, while a person of a very high social status is often wearing clothing that is physically less practical than those of the working class.
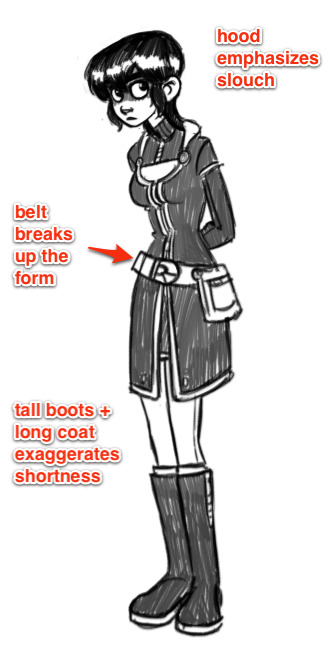
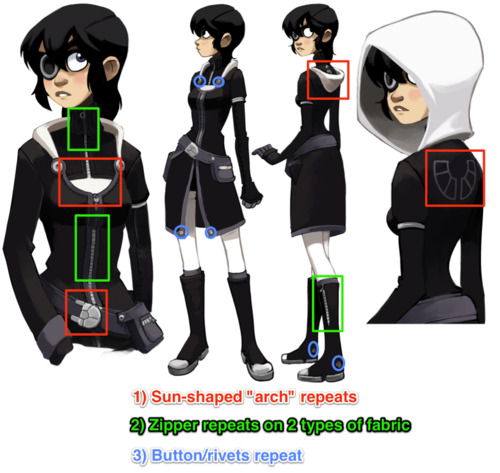
How does your character move? What are their default postures and body language? A good outfit should accentuate the body movements that you deem most important. If a character stoops and hunches a lot, their clothes can augment that behavior. For example, Kim is frequently hunched over, so I tend to dress her with a hood that’s shaped to go with poor posture, as well as a repeating “arch” shape to suggest this basic form.
Communication
How much does the character wish to communicate with their clothing? Not everyone wears their personality on their sleeve, nor is everyone especially fashion-conscious. Nothing’s worse than having a cast where everyone is immaculately dressed and overdesigned. A more outgoing character might be more aware of their appearance, while a more introverted one may be less concerned. To add another layer, a character may dress a certain way to disguise something they don’t want to show to others, just as someone might act overconfidently to hide their insecurities. You can tell your audience a lot about your character through what that character chooses to display to others.
Repetition
Core shapes and patterns should repeat on the outfit. The entire design should exhibit some bilateral cohesion, which is to say if you were to cut the character in half horizontally or vertically, each part should look like it belongs to the other.
As mentioned, Kim has a lot of solid colors and arch shapes which are broken up by fabric and metal seams, with very few sharp edges.
Vonnie, on the other hand, is structured almost like a building, with vertical lines and triangles that take the shape of supporting beams on the surface of her outfit. Her triangles and broad horizontal planes repeat throughout her outfit, including her glasses.
This extends to multiple costumes worn by the same character. Even if a particular character changes clothes, the core shapes should still be evident. Scott Pilgrim is a good example of this. Most of the cast change clothes frequently, but in each scene it’s generally easy to recognize the characters by the “type” of clothing they choose. The details change, but the essential shapes do not.
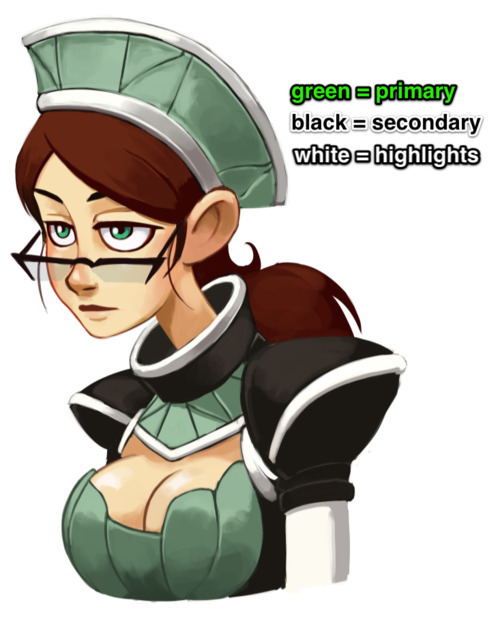
Color and Contrast
Different colors can imply different moods. ”Winter” colors like cooler blues and purples can suggest an introspective or reserved personality, while warmer colors like yellow or red can imply a more energetic attitude. If your character only ever interacts in one type of setting, you only have to worry about how those colors will fit in one environmental color palette. If, however, your character needs to mesh well with more than one environment (as is usually the case with protagonists), you have to make sure your character’s colors will fit with multiple settings.
Also, don’t be fooled by superhero comics: it’s generally bad form to have two dominant colors in a single costume. My personal rule of thumb is to have no more than one prime color in an outfit design, followed by a secondary and then supporting colors.
In the case of Kim’s outfit in Dark Science, the primary color is black, with the secondary being off-white. These are then supported by the muted blue and silver accents that appear in both her prosthetics and clothing. Color and value contrast is very important, especially for a main character, which is why Kim’s basic palette can be reduced to black and white without losing any essential information.
Vonnie’s outfit is more colorful, but less contrasted as a whole. Green dominates and is blocked in by a secondary, warmer black. Green is the complementary color of red, and so her clothes naturally bring attention to her hair and reddish skin tone, inherently highlighting more sexual elements than Kim (whose black outfit essentially matches her hair). White is also present, but it’s only a supporting color here.
Simplicity
Above all else, keep it simple. Comic characters are not pin-ups or other illustrations; you have to draw them over and over again, from various angles. If you pile on too much detail, you’ll wear yourself out slogging through all the bits every time you have to draw them.
If you follow all these rules, good costume design should create this basic pattern when presented to a reader:
- Read: Silhouettes and essential shapes should be instantly recognizable
- Inform: The costume should then tell the reader essential things about the character
- Compel: The costume should then invite the reader to learn more about the character
- Move: The costume should never impede the flow of action within the comic
If you stick to these basic guidelines, you’ll never fail. Next up on character design: bodies and faces!